Introduction to Laser Cleaning Technology
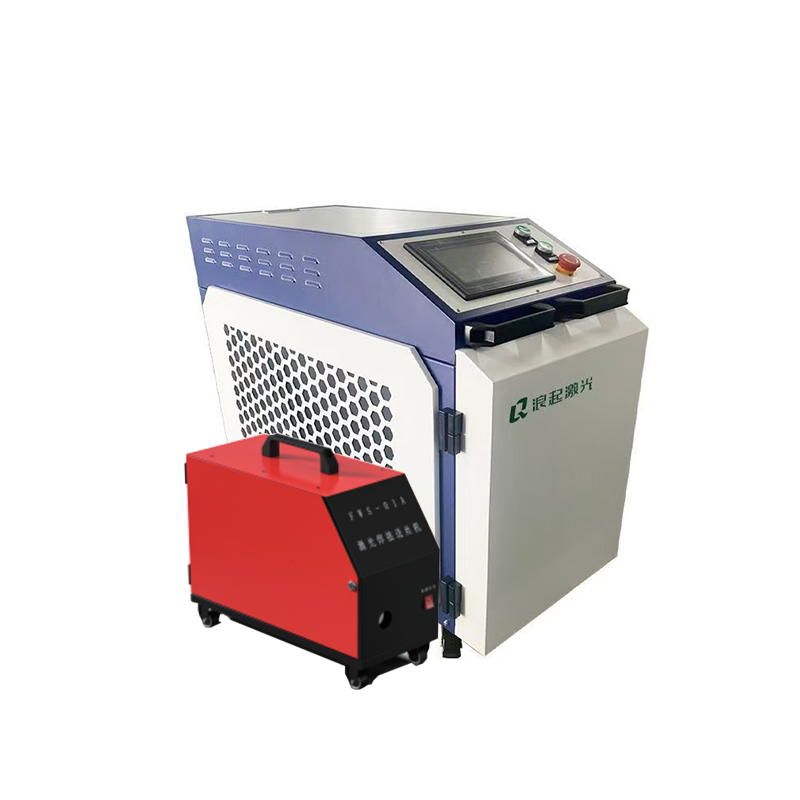
High-power laser cleaning machines represent an advanced surface treatment technology that uses laser beams to remove contaminants, oxides, coatings, and other unwanted materials from surfaces. This non-contact, eco-friendly method offers significant advantages over traditional cleaning techniques like sandblasting or chemical cleaning.
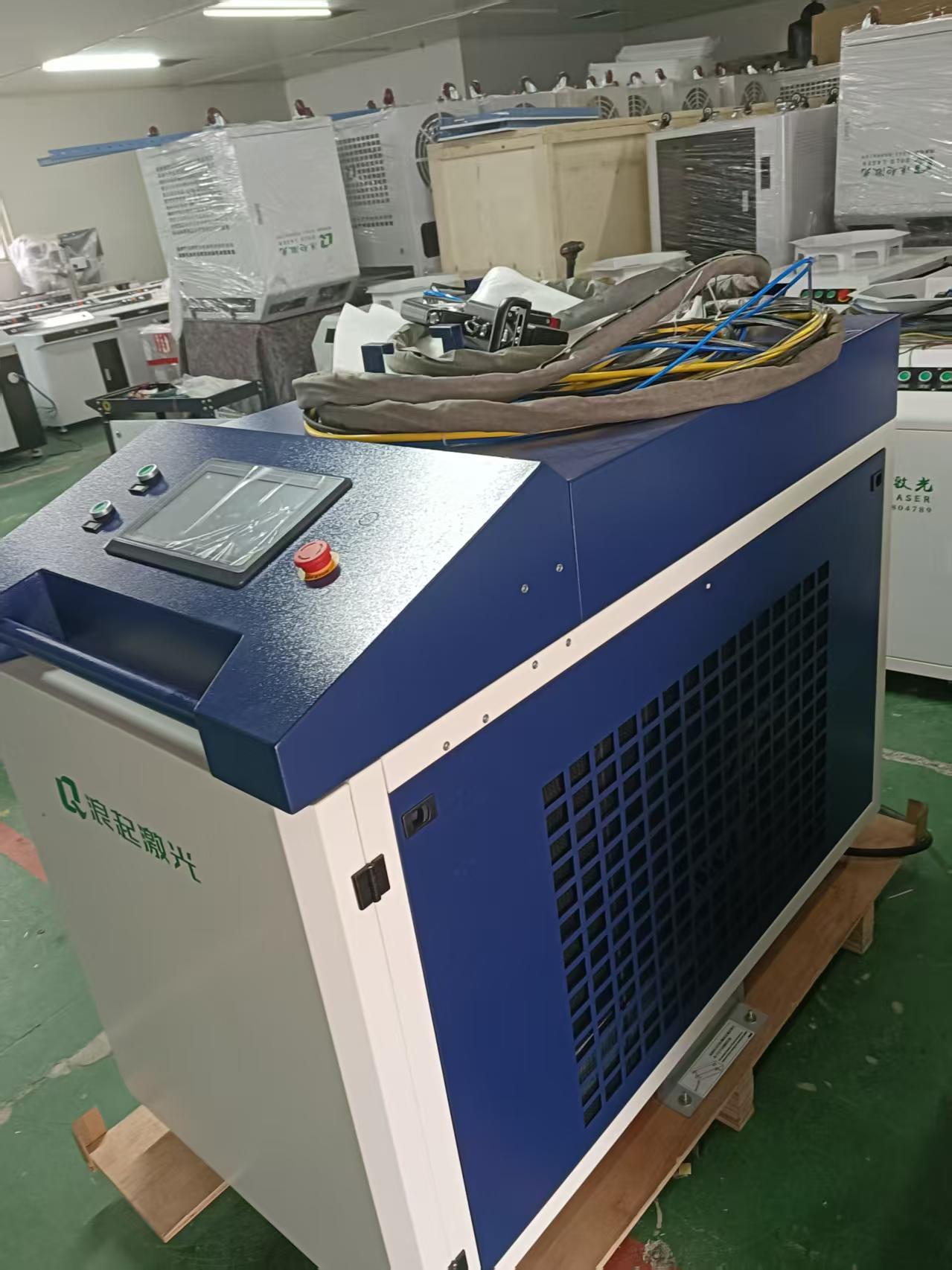
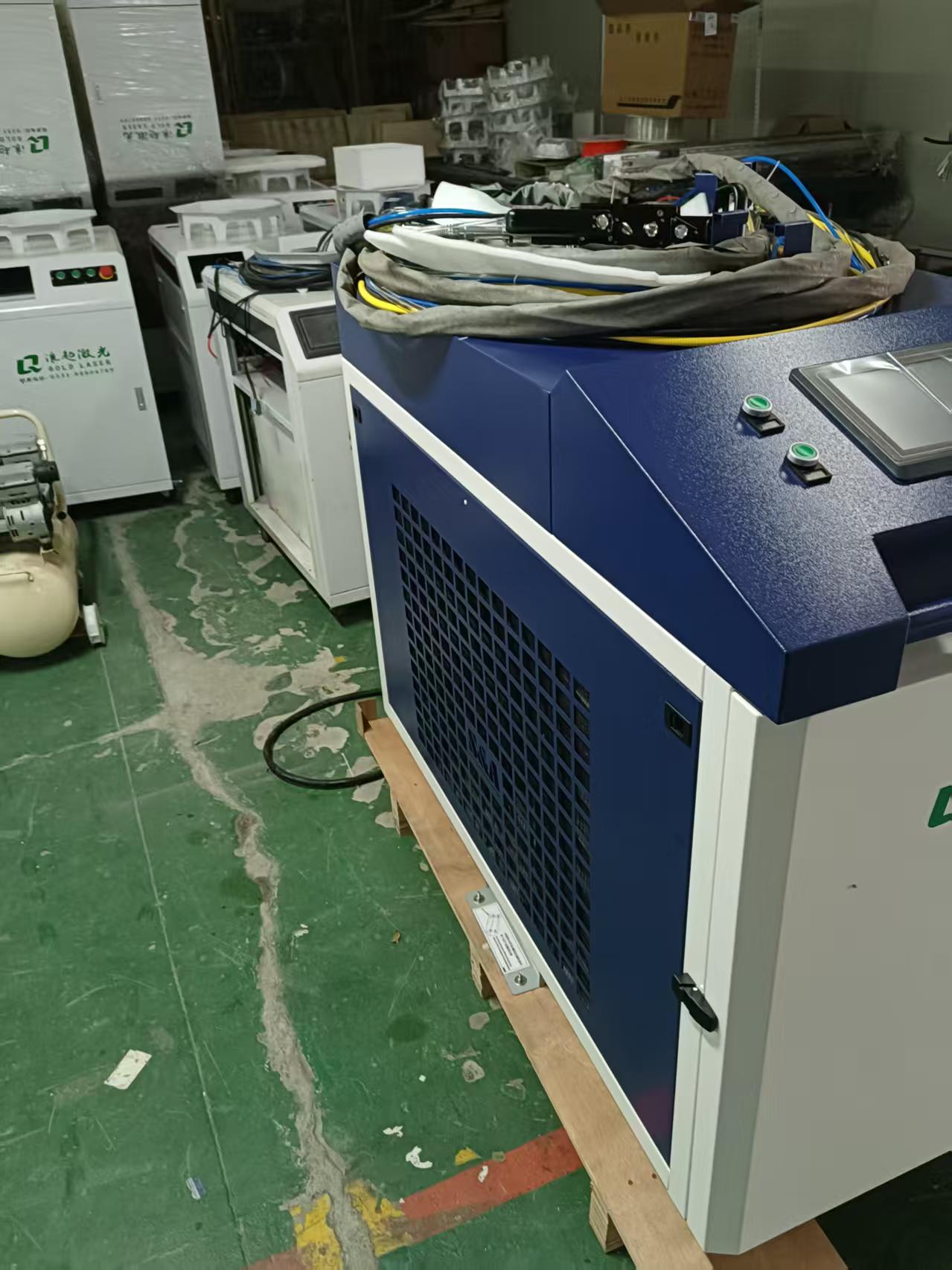
Key Components of High-Power Laser Cleaning Systems
Laser Source: Typically fiber lasers with power ranging from 100W to several kilowatts
Scanning System: Galvanometer scanners or robotic arms for beam delivery
Cooling System: Essential for maintaining optimal laser performance
Fume Extraction: Removes particles and gases generated during cleaning
Control Software: For parameter adjustment and process automation
Optimal Operation Procedures
Pre-Operation Preparation
Conduct thorough safety checks on all system components
Verify proper cooling system operation
Ensure adequate ventilation and fume extraction
Calibrate the laser focusing system
Select appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)
Parameter Optimization
Power Settings: Adjust based on material and contamination type (typically 50-1000W)
Pulse Frequency: Optimize for specific applications (20-2000kHz)
Scan Speed: Balance between cleaning effectiveness and process time
Spot Size: Adjust according to surface area and precision requirements
Overlap Rate: Typically 20-50% for uniform cleaning
Best Practices for Efficient Utilization
Material Compatibility Assessment
Evaluate substrate and contaminant properties before cleaning
Test on sample pieces to determine optimal parameters
Process Optimization
Implement automated path planning for complex geometries
Use multi-pass strategies for thick coatings
Adjust angle of incidence for maximum efficiency
Maintenance Protocols
Regular lens cleaning and optical component inspection
Monitor laser source performance and degradation
Maintain cooling system filters and fluids
Quality Control Measures
Implement real-time monitoring systems
Conduct periodic surface analysis
Document parameters for repeatable results