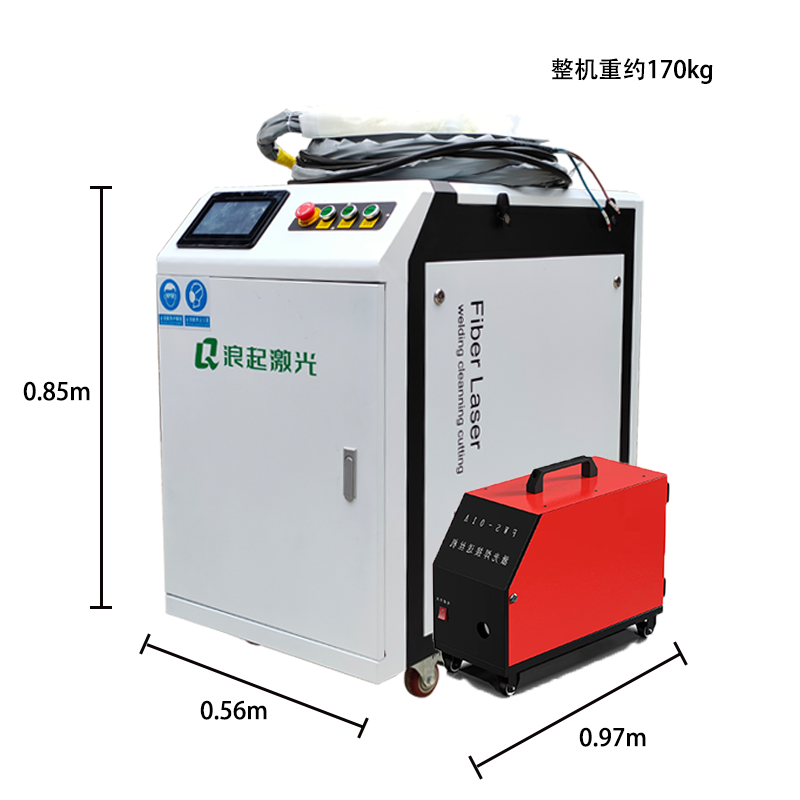
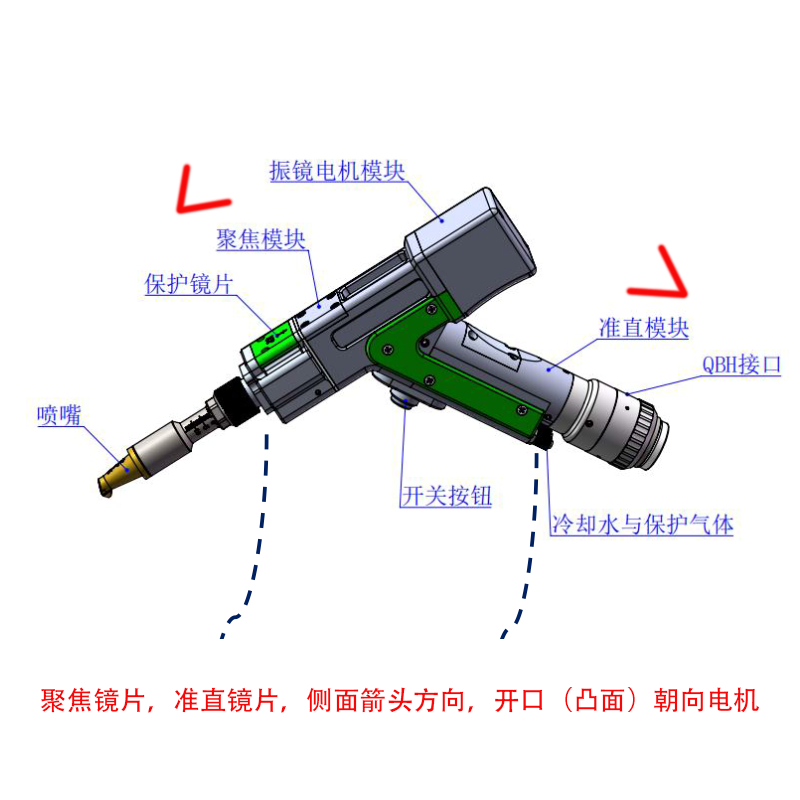
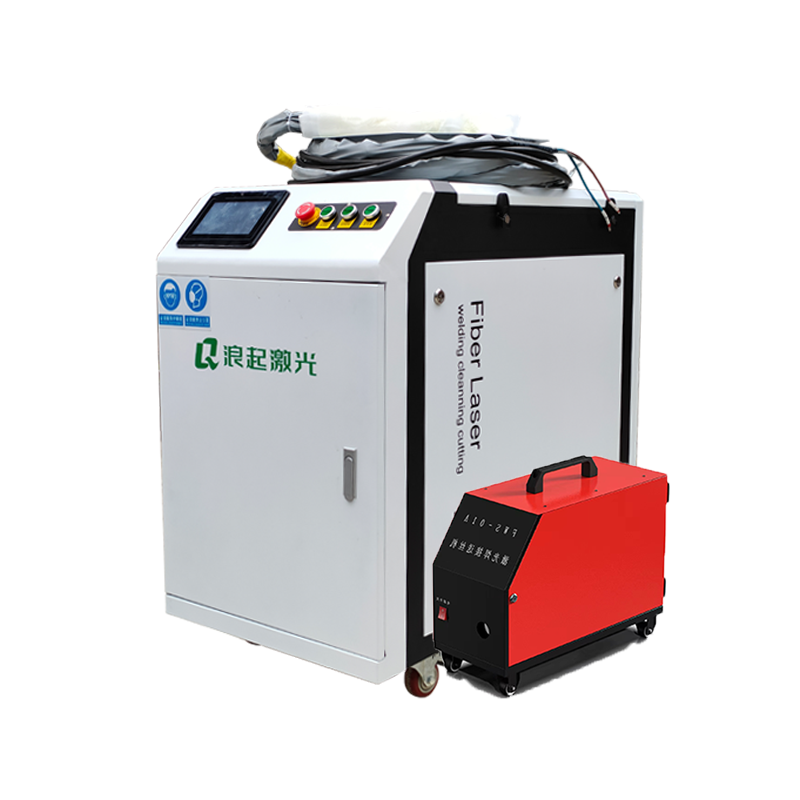
Fiber laser welding machines are highly versatile and capable of welding various types of steel raw materials with precision, speed, and efficiency. Here’s an overview of their capabilities and the types of steel they can weld effectively:

Types of Steel Suitable for Fiber Laser Welding
Carbon Steel (Low/Medium/High Carbon)
Prone to cracking; preheating and post-weld heat treatment may be needed.
Requires controlled heat input to avoid brittleness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ).
Easy to weld due to low carbon content (<0.3%).
Produces strong, crack-free welds with minimal distortion.
Low Carbon Steel (Mild Steel, e.g., AISI 1018, ASTM A36)
Medium Carbon Steel (e.g., AISI 1045)
High Carbon Steel (e.g., AISI 1095, Tool Steels)
Stainless Steel
Requires preheating and post-weld tempering to avoid brittleness.
More challenging due to grain growth; lower power settings may be used.
Excellent weldability, minimal distortion, and good corrosion resistance post-welding.
Austenitic (e.g., 304, 316)
Ferritic (e.g., 430)
Martensitic (e.g., 410, 420)
Alloy Steels
Weld well with fiber lasers, maintaining mechanical properties.
Used in high-strength applications; may need controlled cooling to prevent cracking.
Low-Alloy Steels (e.g., 4140, 4340)
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels
Tool Steels (e.g., D2, H13, A2)
Used in molds, dies, and cutting tools.
Require precise heat control to avoid cracking and maintain hardness.
Galvanized Steel & Coated Steels
Zinc-coated steels can be welded but may require adjustments (e.g., higher speed, gas shielding) to prevent porosity from zinc vaporization.
High-Speed Steel (HSS, e.g., M2, T1)
Used in cutting tools; laser welding helps maintain hardness with minimal HAZ.
Advantages of Fiber Laser Welding for Steel
✔ High Precision – Focused beam allows for narrow, deep welds with minimal distortion.
✔ Speed – Faster than TIG, MIG, or arc welding, improving productivity.
✔ Automation-Friendly – Ideal for robotic integration in industrial applications.
✔ Low Heat Input – Reduces warping, especially in thin materials.
✔ Versatility – Can weld dissimilar steels (e.g., stainless to carbon steel) with proper settings.
Key Considerations for Optimal Welding
Material Thickness: Fiber lasers work best on thin to medium-thickness steel (0.1mm up to ~10mm, depending on laser power).
Gas Shielding (Argon/Helium/Nitrogen) – Prevents oxidation in stainless and high-alloy steels.
Pulse vs. Continuous Wave (CW) Mode – Pulsed lasers are better for thin or heat-sensitive steels.
Joint Preparation – Clean, oxide-free surfaces improve weld quality.
Applications in Industry
Automotive – Body panels, exhaust systems, battery welding.
Aerospace – Thin sheet metal, engine components.
Tool & Die – Repairing molds and cutting tools.
Construction – Structural steel, pipelines (with high-power lasers).