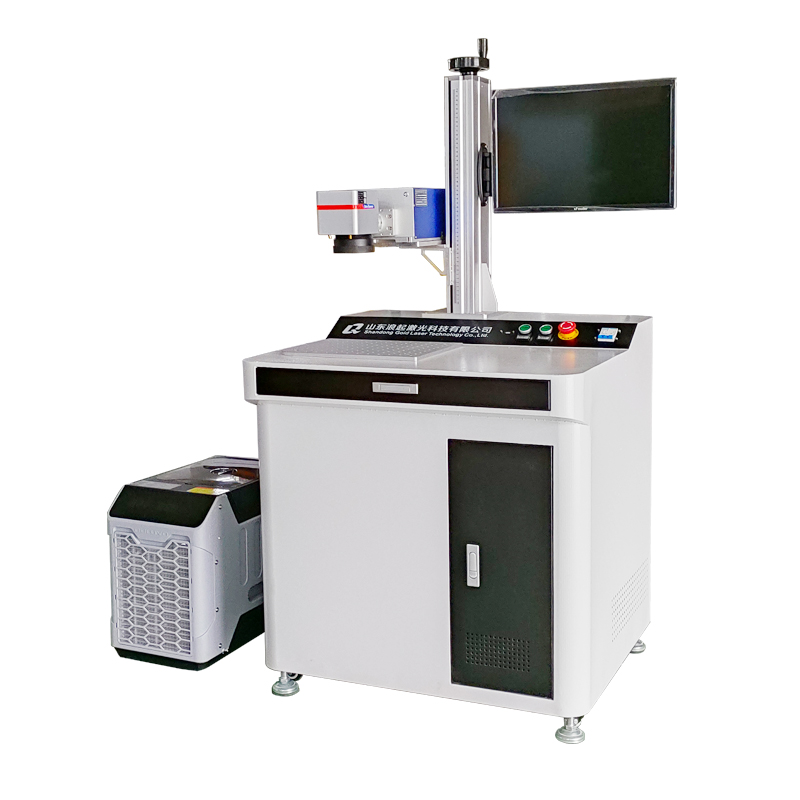
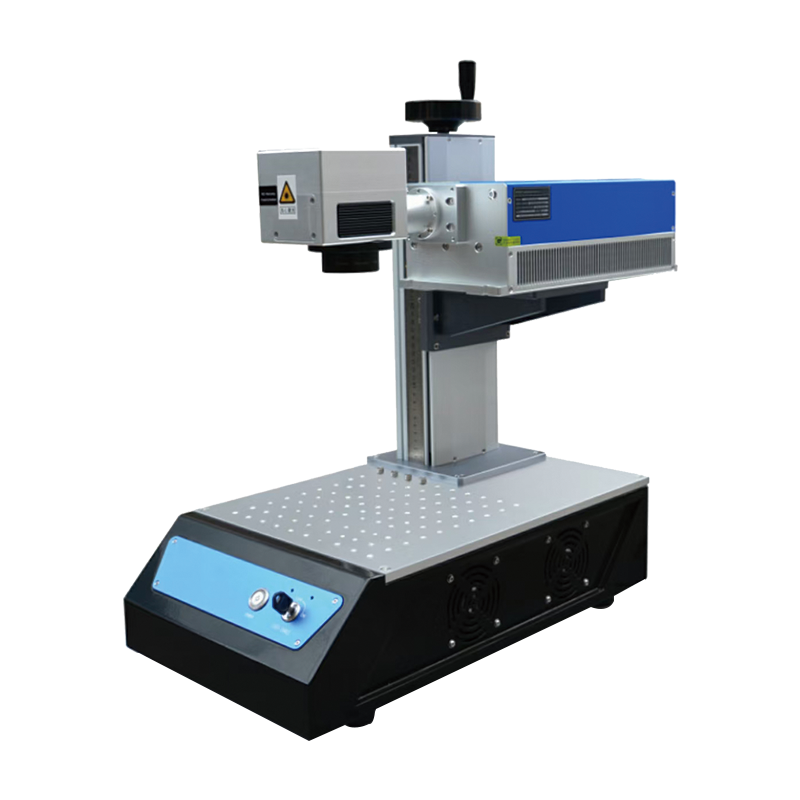
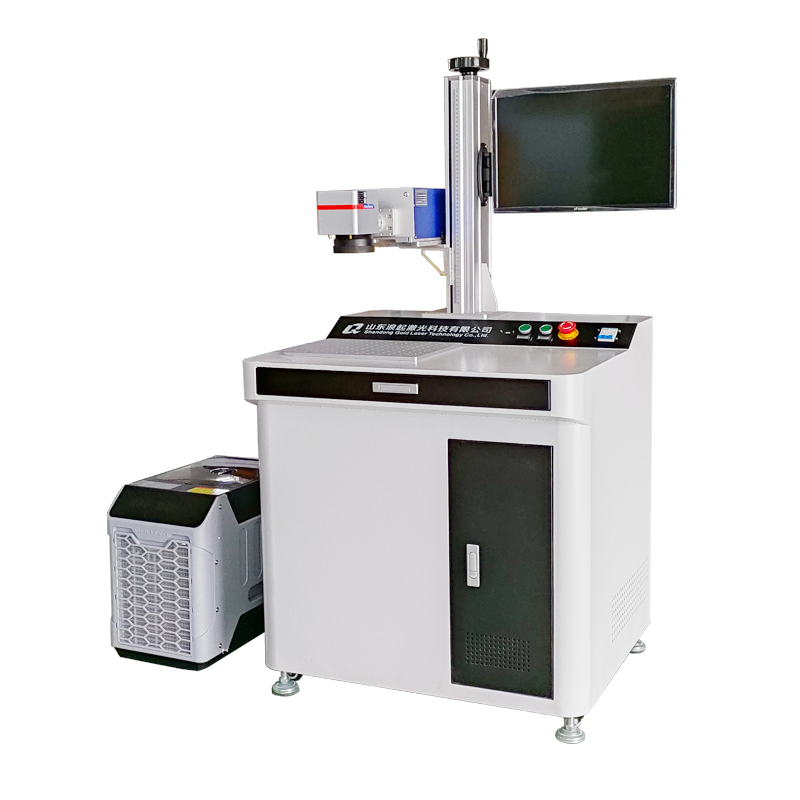
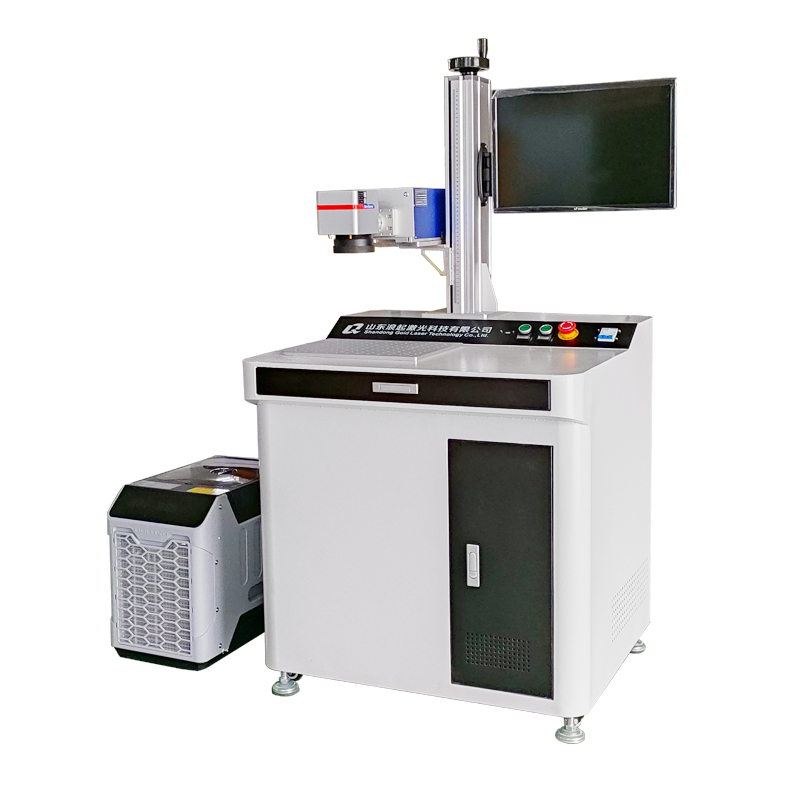
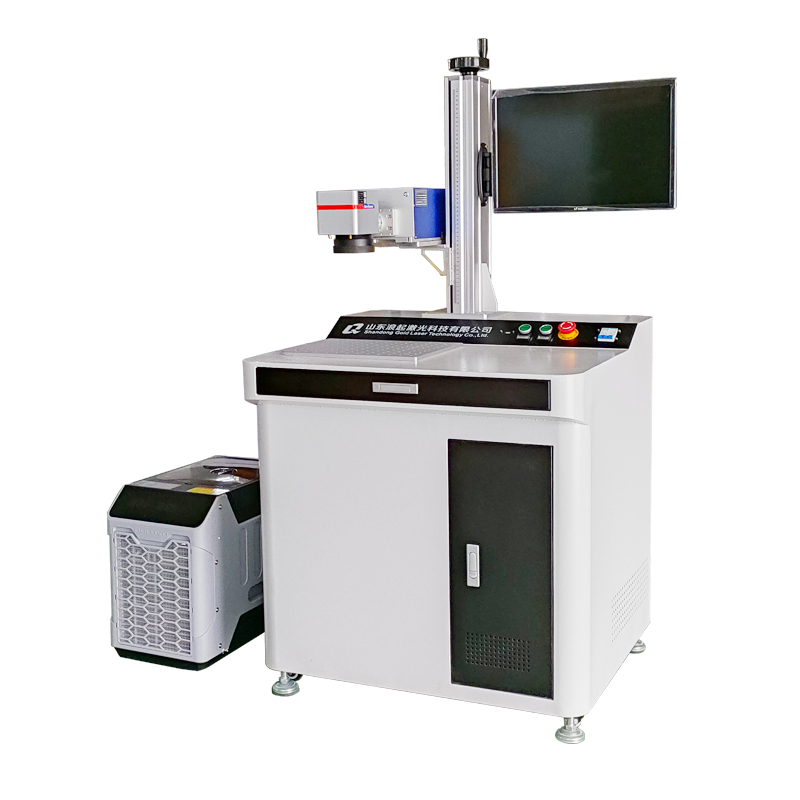
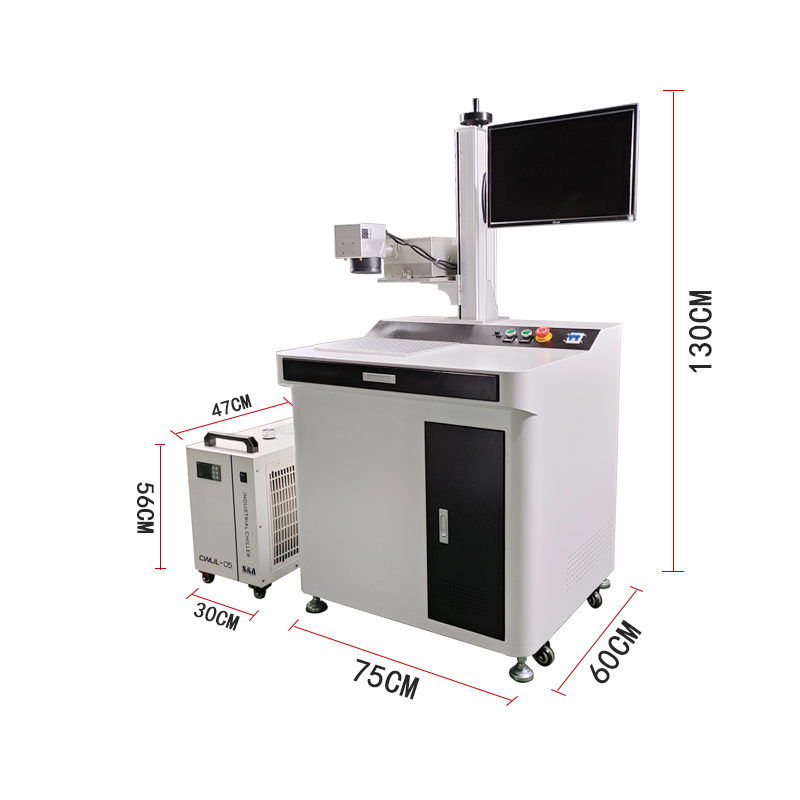
The UV laser marking machine operates based on the principle of cold marking, where a high-energy ultraviolet (UV) laser beam interacts with materials to create precise, high-contrast marks without thermal damage. Here is a breakdown of its operating principle:
1. UV Laser Generation
The machine uses a UV laser source (typically a 355nm wavelength laser), generated via:
Solid-state laser pumping: An infrared laser (e.g., Nd:YAG or Nd:YVO₄ crystal) is frequency-tripled (third harmonic generation) to convert 1064nm IR light into 355nm UV light.
Q-switching: Produces short, high-energy pulses (nanoseconds) for precise material interaction.
2. Material Interaction (Cold Ablation)
UV light has high photon energy (short wavelength), enabling:
Photochemical Breaking of Molecular Bonds: The material absorbs UV photons, directly breaking chemical bonds (non-thermal process).
Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Unlike infrared lasers, UV lasers avoid melting or burning, making them ideal for heat-sensitive materials (e.g., plastics, glass, electronics).
High Absorption: Many materials absorb UV light better than IR, improving marking efficiency.
3. Marking Process
The focused UV laser beam (via galvanometer scanners and F-theta lens) removes or alters surface material in controlled patterns:
Plastics: Breaks polymer chains, leaving clean marks.
Glass/Ceramics: Micro-cracking or surface etching.
Metals: Thin oxide layer formation for dark/light marks.
Engraving: Subtractive process—vaporizes material to create depth.
Annealing/Discoloration: Induces color changes (e.g., on metals or plastics) via oxidation or chemical reactions.
Foaming: On plastics, creates raised marks by gas formation.
Material-Specific Reactions:
4. Key Advantages
High Precision: Resolves fine details (<0.1mm) for 2D codes, logos, or text.
No Consumables: Contactless process, reducing maintenance.
Wide Material Compatibility: Works on plastics, silicone, PCB, glass, metals, and more.
Durability: Marks resist fading, abrasion, and chemicals.
5. Applications
Electronics: PCB marking, microchips.
Medical Devices: Surgical tools, pill marking.
Packaging: Food-safe plastic/glass labeling.
Jewelry: Precision engraving without heat damage.